android sdk
This documentation highlights the requirements for using the paymennt Android SDK. Throughout this document, we aassume that you are using Android Studio for your Android development.
The minimum supported Android API level for the SDK is 16 (KitKat), however, setting the minimum Android API level to 26 (Pie) is recommended.
The SDK uses Google's SafetyNet API for security, setting minimum Android API to lower than 26 will prevent it from functioning.
Setting up the SDK
JitPack Repository
Include the JitPack.io repository to your Android project in your_project_home/build.gradle
allprojects {
repositories {
...
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
flatDir {
dirs 'libs'
}
}
}
paymennt SDK Dependency
Include the paymennt Android SDK dependency to your project in your_project_home/app/build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.pointcheckout:android-sdk:v1.3'
}
Required Permissions
The paymennt SDK requires the following permissions. Please add them to your AndroidManifest.xml file if they are not already present:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
Adding SafetyNet Support
You must add Google's SafetyNet API to your app/build.gradle. For details on how to add SafetyNet to your project, follow the instructions found in this guide.
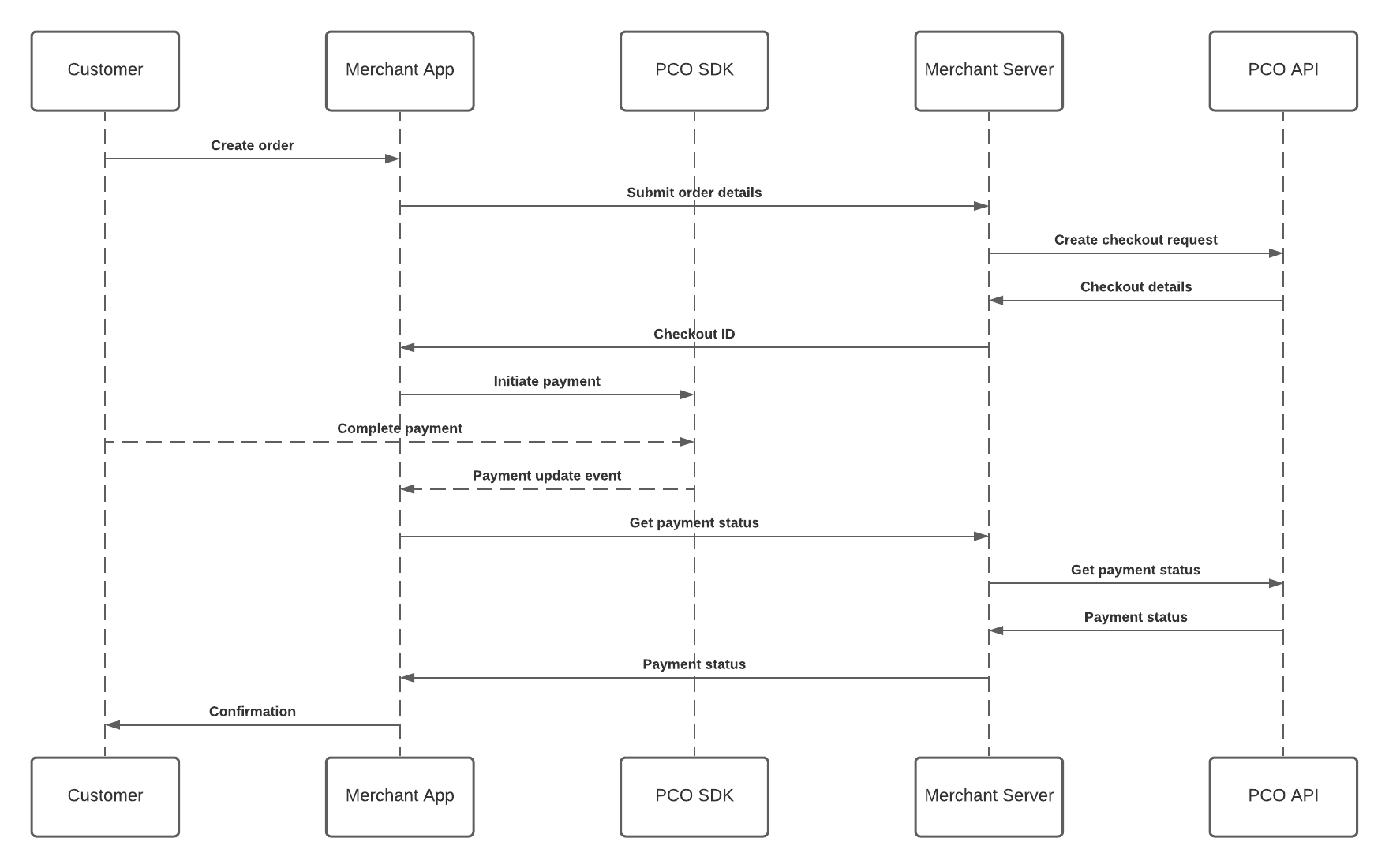
SDK Flow
The paymennt Android SDK requires three distinct steps for you to accept card payments:
- Create a new mobile Checkout
- Initiate the PointCheckoutClient from the SDK using the provided checkout key
- Query the API for the payment status
This diagram shows the overall payment and data flow in order to accept payments using the paymennt mobile SDK
Using the SDK
Create a new mobile checkout request
Send new checkout request to Create mobile checkout API. Check mobile payment integration guide for more details.
API calls made to the paymennt API endpoints should be made from your server. You should NEVER include your API keys in your mobile application. A malicious user can gain access to your account if those keys are exposed.
Create a new the PointCheckoutClient
Create an object of PointCheckoutClient pointing to the required environment.
PointCheckoutClient pcoClient = new PointCheckoutClient(environment);
| Environment | Description |
|---|---|
Enviornment.PRODUCTION | Use this for accepting customer payments |
Enviornment.TEST | Use this during integration testing |
Keep a reference of the created client to reuse the same instance
Initialize
Initialize the created PointCheckoutClient using:
pcoClient.initialize(context);
Invoke the initialize method when the app starts as it requires 2-3 seconds to initialize the SDK. If the client is not initialized and pay is called, the client will call initialize internally before calling pay resulting in delay.
Start the Payment Process
To commence the payment process, you must call the static pay method of the PointCheckoutClient. This method accepts 3 parameters:
contextwhich refers to the current activity contextcheckoutKeyreceived in the Create mobile checkout API call.listenerthat will be called on payment update or cancellation
pcClient.pay(context, checkoutKey, new PointCheckoutEventListener() {
@Override
public void onUpdate() {
System.out.println("UPDATE CALLBACK");
}
@Override
public void onDismiss() {
System.out.println("USER CLOSED THE MODAL");
}
});
Calling the pay function will open a modal where the user will be able to complete the payment in a secure manner.
Listen to Payment Events
The PointCheckoutEventListener event listener has two callbacks:
onUpdatewhich is called the checkout status is updated (paid, cancelled, failed .etc). You MUST call paymennt API to fetch the new status of the checkout to verify that its been successfully paid.onDismisswhich is called if the user closes the modal by clicking on close button.
Retrieve Checkout Status
Retrieve checkout status and details using the Get checkout API call. Check mobile payment integration guide for more details.
API calls made to the paymennt API endpoints should be made from your server. You should NEVER include your API keys in your mobile application. A malicious user can gain access to your account if those keys are exposed.